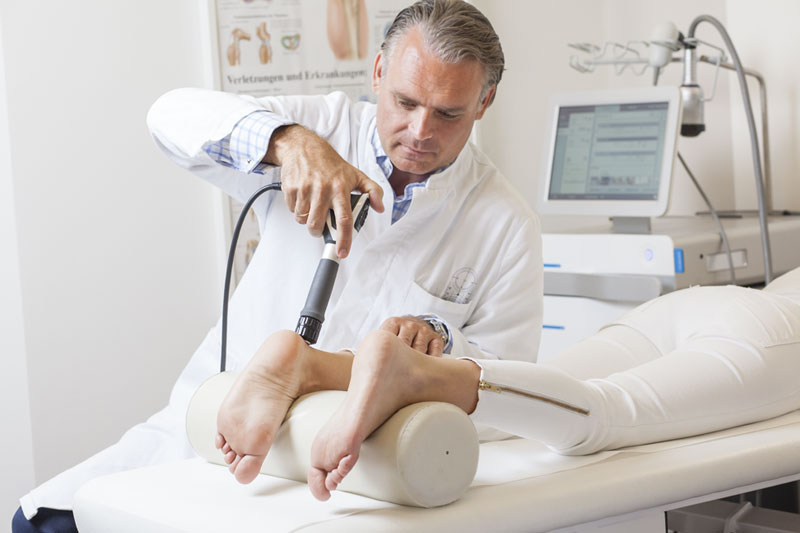
SHOCKWAVE THERAPY

SHOCKWAVE THERAPY
- Focused shockwave therapy (F-SW)
- Radial shockwave therapy (R-SW)
- V-Actor vibration therapy
Indications:
- Shoulder pain, e.g. calcific tendonitis
- Tennis or golfer’s elbow
- Jumper’s knee
- Shin splints/tibial stress syndrome
- Achilles tendon pain (achillodynia)
- Heel pain/heel spur
How does extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) work?
Shockwaves are short, high-energy acoustic waves that can penetrate or tissues containing water without being weakened. They can also penetrate elastic body tissues such as muscles and fat. The shockwaves only discharge their energy when they hit hard tissue such as kidney stones, gallstones or calcific deposits in tendons and break them down.
A device is used to generate the shockwaves externally, then they are transferred to the body via a water-filled cushion. This allows the therapist to concentrate all the energy from the waves into a single point, similar to a magnifying glass. In this way, the shockwaves can be targeted precisely at the area that requires treatment. The shockwaves can be prevented from reaching other body tissues and the focus can be precisely calculated. It is possible to target the shockwaves on a specific zone, in order to avoid unwanted side effects.
Shockwave therapy (ESWT) as a non-invasive alternative to surgery
Shockwave therapy has now been available for just over ten years. It can be a non-invasive way of treating inflammation, calcification and injury. Shockwave therapy has almost zero side effects and can often replace the need for surgery.
Intensive research has been carried out into how shockwave therapy works.
Numerous studies have provided clear evidence of its clinical effectiveness.
It changes the milieu of the tissue that is treated and can stimulate regeneration by releasing healing bone-forming neurotransmitters.
Shockwaves were originally used to remove kidney stones and gallstones without the need for surgery. In the past an operation was always required, but now such problems can often be treated in a non-invasive way using extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT).